
Customized products can be provided according to drawings
Gravity Die Casting


What is Gravity Die Casting?
-Gravity Die Casting Materials
Gravity die casting is suitable for a variety of non-ferrous metals and some ferrous metals, each of which has its own unique properties and application areas. Selecting the right material can ensure the quality and performance of the final product while meeting the requirements of cost-effectiveness. Whether in the automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics or industrial equipment fields, gravity die casting is a reliable manufacturing process.
Material | Key Features |
Aluminum Alloys | Lightweight/ High strength/ Corrosion resistant/ Good thermalconductivity |
Magnesium Alloys | Extremely lightweight/ Good mechanical properties/ Excellent damping capacity |
Zinc Alloys | High density/ Easy to cast/ Good mechanical properties/ Excellent surface finish |
Gray Cast Iron | Good wear resistance/ Excellent vibration damping/ Low cost |
Ductile Iron | High strength and toughness/ Good wear resistance |
Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance/ High temperature performance |
Copper Alloys | Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity/ Good corrosion resistance |
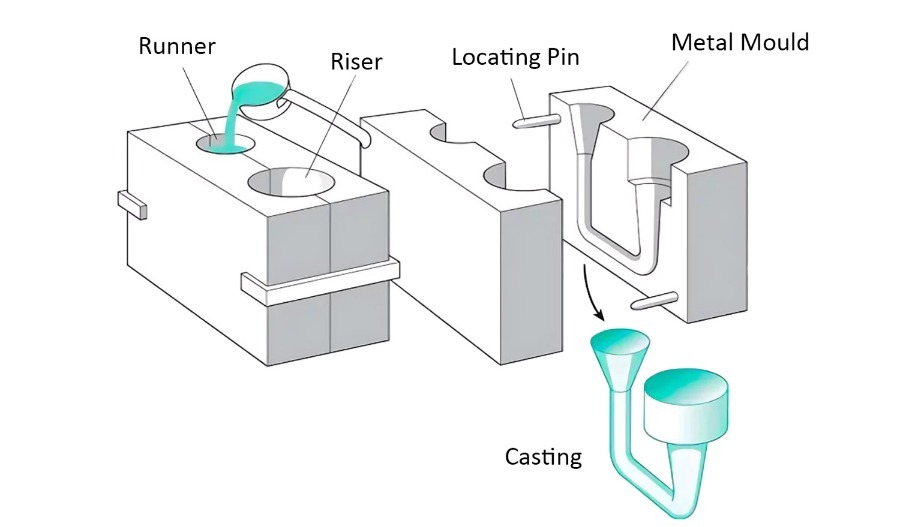
Gravity Die Casting Step By Step
1. Mold Preparation
● The mold, typically made of high-strength steel, consists of two halves that can open and close.
● Before pouring, the mold heats to a specific temperature to ensure uniform heat distribution and prevent thermal shock to the mold material.
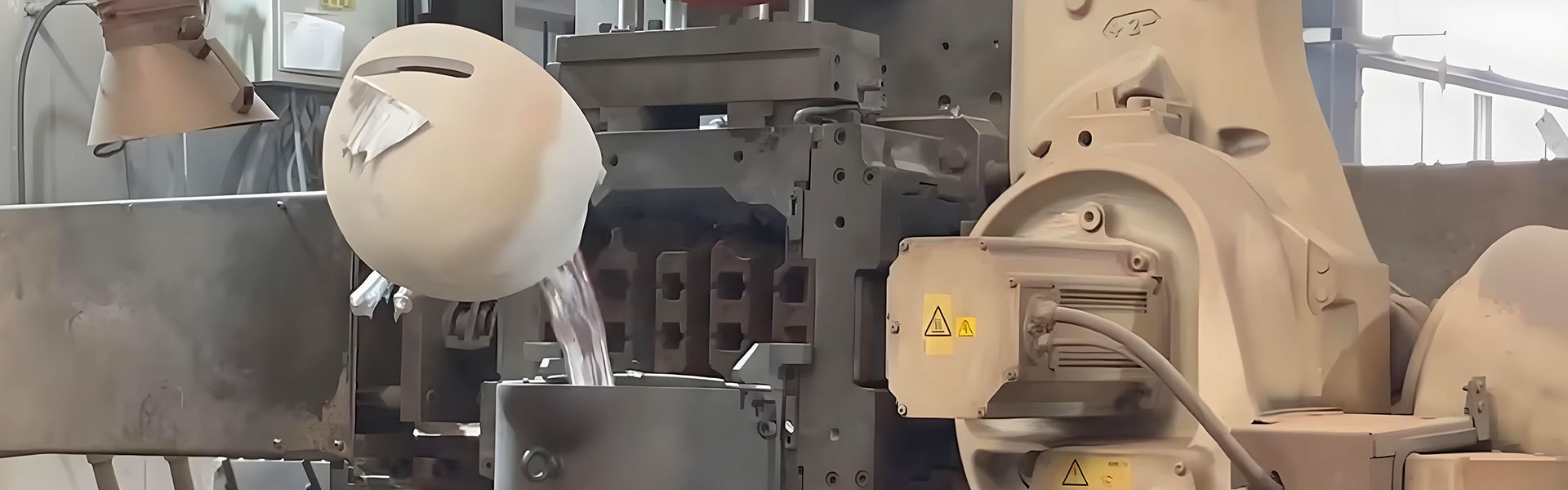
2. Pouring
● Molten metal pours into the mold through a pouring spout or gating system.
● The metal flows into the mold cavity under the influence of gravity, filling the voids and taking the shape of the desired part.
3. Solidification
● The molten metal cools and solidifies within the mold.
● Controlled cooling rates can be achieved by adjusting the mold temperature and using cooling channels.
4. Ejection
● Once the metal has solidified, the mold halves separate, and the casting ejects using ejector pins.
● The part is then removed from the mold, and any excess material, such as gates and risers, is trimmed off.
5. Post-Processing
● The cast part may undergo additional processes like machining, surface treatment, or assembly to meet specific requirements.
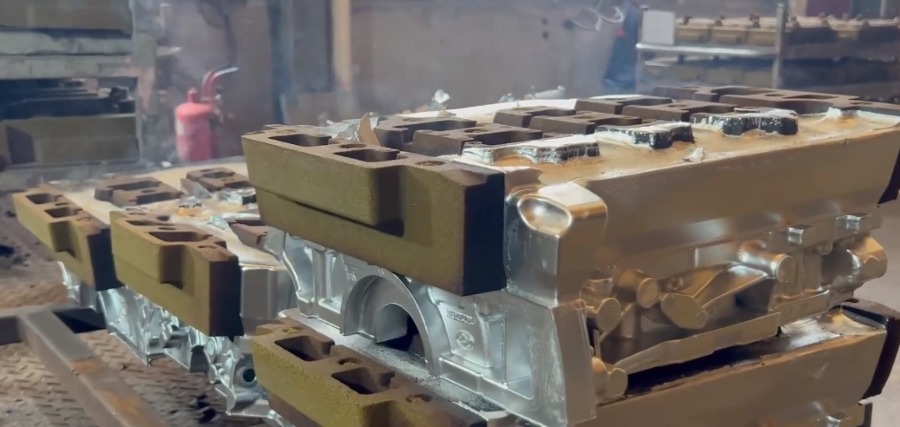
Gravity Die Casting Applications
1. For vehicles. Parts such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission cases benefit from the precision and strength provided by this method.
2. Aerospace: In aerospace, the need for lightweight yet strong parts is paramount. Gravity die casting helps in producing intricate components like turbine blades and structural parts that meet stringent safety and performance standards.
3. Electronics: For electronic devices, gravity die casting ensures the production of enclosures and heat sinks with excellent thermal conductivity and tight tolerances, essential for efficient cooling and compact design.
4. Medical Equipment: Precision and reliability are critical in medical applications. This casting method enables the creation of surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment parts, and other medical devices that require high accuracy and quality.
5. Consumer Goods: From cookware to home appliances, gravity die casting allows for the mass production of durable, aesthetically pleasing items. The process supports the creation of intricate designs and smooth finishes, enhancing product appeal.
6. Construction: In the construction industry, gravity die casting contributes to the fabrication of hardware like door handles, hinges, and plumbing fixtures, ensuring robustness and longevity.
7. Lighting: For lighting fixtures, this technique ensures components are both functional and decorative, capable of achieving the necessary electrical insulation properties and aesthetic requirements.
8. Sports and Leisure: Equipment such as golf club heads, fishing reels, and bicycle components can be manufactured using gravity die casting, providing the necessary strength and weight distribution for optimal performance.

The Advantages & Disadvantages of Gravity Die Casting
- Advantages of Gravity Die Casting
1. Precision and Detail: Gravity die casting allows for high precision in part dimensions and intricate details, making it suitable for complex shapes.
2. Surface Finish: Parts produced through this method often have a better surface finish compared to sand casting, reducing the need for additional machining.
3. Material Versatility: The process can handle various metals, including aluminum, zinc, and copper alloys, offering flexibility in material selection.
4. Economic Efficiency: For medium to large production runs, gravity die casting can be cost-effective due to the long life of the tooling and the ability to produce multiple parts quickly.
5. Environmental Impact: Since the process uses gravity instead of high pressure, it consumes less energy and produces fewer emissions.
- Disadvantages of Gravity Die Casting
1. Tooling Cost: Initial setup and tooling costs for gravity die casting can be high, especially for complex molds or large-scale production.
2. Size Limitations: The size of parts that can be produced is limited by the capacity of the casting machine and the mold design.
3. Cooling Rate Variability: Different areas of the cast part may cool at different rates, leading to potential issues like warping or internal stresses.
4. Porosity Issues: Gas entrapment during the pouring process can cause porosity in the final product, affecting its strength and durability.
5. Production Speed: Compared to high-pressure die casting, gravity die casting has a slower production rate, which can be a disadvantage for very high-volume production needs.
We would be happy to connect with you.
We will contact you within one working day. Please pay attention to your email.







